18장 함수와 일급 객체
1 일급 객체
다음과 같은 조건을 만족하는 객체를 일급 객체라 한다.
무명의 리터럴로 생성할 수 있다. 즉, 런타임에 생성이 가능하다.
변수나 자료구조(객체, 배열 등)에 저장할 수 있다.
함수의 매개변수에 전달할 수 있다.
함수의 반환값으로 사용할 수 있다.
// [예제 18-01]
// 1. 함수는 무명의 리터럴로 생성할 수 있다.
// 2. 함수는 변수에 저장할 수 있다.
// 런타임(할당 단계)에 함수 리터럴이 평가되어 함수 객체가 생성되고 변수에 할당된다.
const increase = function (num) {
return ++num;
}
const decrease = function (num) {
return --num;
}
// 2. 함수는 객체에 저장할 수 있다.
const auxs = { increase, decrease };
// 3. 함수는 매개변수에 전달할 수 있다.
// 4. 함수의 반환값으로 사용할 수 있다.
function makeCounter(aux) {
let num = 0;
return function () {
num = aux(num);
return num;
};
}
// 3. 함수는 매개변수에게 함수를 전달할 수 있다.
const increaser = makeCounter(auxs.increase);
console.log(increaser()); // 1
console.log(increaser()); // 2
// 3. 함수는 매개변수에게 함수를 전달할 수 있다.
const decreaser = makeCounter(auxs.decrease);
console.log(decreaser()); // -1
console.log(decreaser()); // -2
2 함수 객체의 프로퍼티
함수는 객체다. 따라서 함수도 프로퍼티를 가질 수 있다.
function square(number) {
return number * number;
}
console.dir(square);
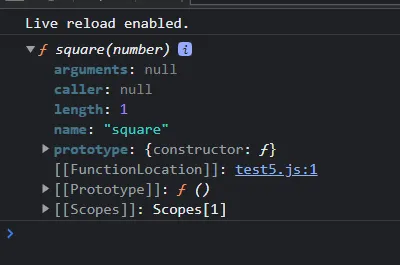
2.1 arguments 프로퍼티
arguments객체는 순회 가능한 유사 배열 (for, arr)이다. 유사 배열 객체란 length 프로퍼티를 가진 객체로 for 문으로 순회할 수 있는 객체를 말한다.
function multiply(x, y) {
console.log(arguments);
return x * y;
}
console.log(multiply()); // [Arguments] {} NaN
console.log(multiply(1)); // [Arguments] { '0': 1 } NaN
console.log(multiply(1, 2)); // [Arguments] { '0': 1, '1': 2 } 2
console.log(multiply(1, 2, 3)); // [Arguments] { '0': 1, '1': 2, '2': 3 } 2
// 매개변수의 개수보다 인수를 더 많이 전달한 경우 초과된 인수도 arguments 객체에 포함된다.
매개변수 개수를 확정할 수 없는 가변 인자 함수를 구현할 때 유용하다.
// [예제 18-06]
function sum() {
let res = 0;
// arguments 객체는 length 프로퍼티가 있는 유사 배열 객체이므로 for 문으로 순회할 수 있다.
for (let i = 0; i< arguments.length; i++){
res += arguments[i];
}
return res;
}
2.2 caller 프로퍼티
caller 프로퍼티는 함수 자신을 호출한 함수를 가리킨다.
// [예제 18-09]
function foo(func){
return func();
}
function bar(){
return 'caller : ' + bar.caller;
}
// 브라우저에서의 실행한 결과
console.log(foo(bar)); // caller : function foo(func) {...}
console.log(bar()); // caller : null
2.3 length 프로퍼티
함수를 정의할 때 선언한 매개변수의 개수를 가리킨다.
// [예제 18-10]
function foo(){}
console.log(foo.length); // 0
function bar(x){
return x;
}
console.log(bar.length); // 1
function baz(x, y) {
return x * y;
}
console.log(baz.length); // 2
2.4 name 프로퍼티
함수 객체의 name 프로퍼티는 함수 이름을 나타낸다.
// [예제 18-11]
// 기명 함수 표현식
var namedFunc = function foo(){};
console.log(namedFunc.name); // foo
// 익명 함수 표현식
var anonymousFunc = function(){};
// ES5 : name 프로퍼티는 빈 문자열을 값으로 갖는다.
// ES6 : name 프로퍼티는 함수 객체를 가리키는 변수 이름을 값으로 갖는다.
console.log(anonymousFunc.name); // anonymousFunc
// 함수 선언문(Function declaration)
function bar() {}
console.log(bar.name); // bar
2.5 **proto **접근자 프로퍼티
모든 객체는 [[Prototype]]이라는 내부 슬롯을 갖는다. 이 슬롯은 객체지향 프로그래밍의 상속을 구현하는 프로토타입 객체를 가리킨다.
// [예제 18-12]
const obj = { a:1 };
// 객체 리터럴 방식으로 생성한 객체의 프로토타입 객체는 Object.prototype이다.
console.log(obj.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
// 객체 리터럴 방식으로 생성한 객체는 프로토타입 객체인 Object.prototype의 프로퍼티를 상속받는다.
// hasOwnProperty 메소드는 Object.prototype의 메소드이다.
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty('a')); // true
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty('__proto__')); // false
hasOwnProperty 메소드
이름에서 알 수 있듯이 인수로 전달받은 프로퍼티 키가 객체 고유의 프로퍼티 키인 경우에만 true를 반환하고 상속받은 프로토타입의 프로퍼티인 경우 false를 반환한다.
2.6 prototype 프로퍼티
prototype 프로퍼티는 생성자 함수로 호출할 수 있는 함수 객체, 즉 constructor 생성자만이 소유하는 프로퍼티이다. 생성자 함수로 호출할 수없으면 해당 프로퍼티가 없다.
// [예제 18-13]
// 함수 객체는 prototype 프로퍼티를 소유한다.
(function (){}).hasOwnProperty('prototype'); // => true
// 일반 객체는 prototype 프로퍼트를 소유하지 않는다.
({}).hasOwnProperty('prototype'); // => false
Last modified: 22 December 2024